Composite Materials for 3D Printing
Composites and Continuous Fibre Reinforcement | Strong, Affordable Printing
- Composite materials combine two or more materials to create a stronger and often lighter final product.
- In 3D printing, there are two main types of composite materials: chopped and continuous.
- Chopped fibre composite materials have small strands of fibre mixed into the plastic base material, making the material stiffer as the percentage of fibre increases.
- Continuous fibre composite materials involve long strands of fibre, such as carbon fibre, fibreglass, or kevlar, mixed with a plastic filament during the printing process.
- Carbon-fibre reinforced composites, for example, can exhibit strength comparable to aluminium while being printed at a lower cost.
- Companies like NASA, Google, and Ford are utilizing Markforged’s continuous carbon fibre industrial printer platform to create parts that are up to 23 times stronger and can be printed 50 times faster than ABS.
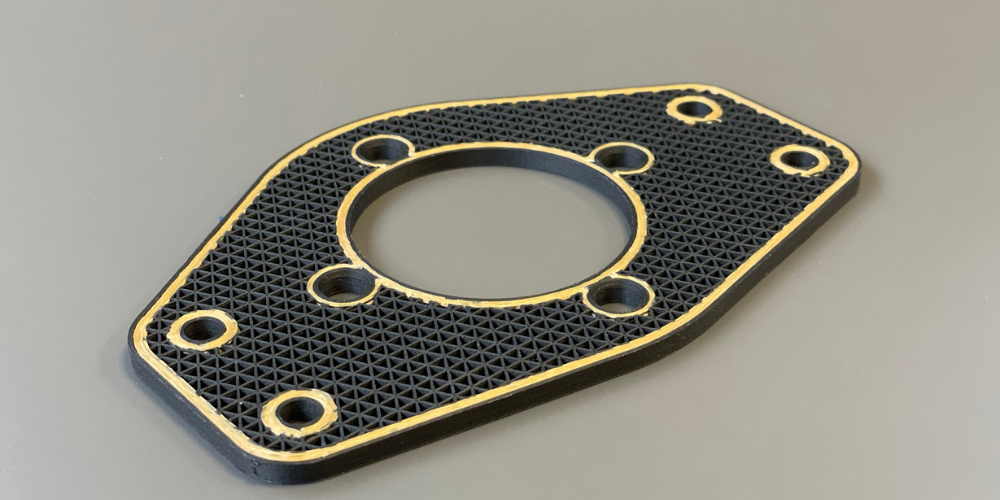
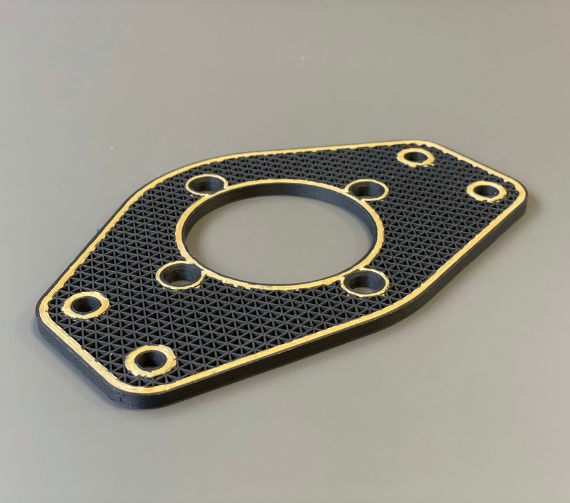
What can you print with composite and carbon fibre reinforcement?





Interested in Composite and Continuous Fibre Reinforced 3D printing?
Want to know if your application is suitable for Composites or CFR 3D Printing?
Which Markforged Composite Material?
Onyx™
Engineering grade thermoplastic, micro carbon fibre filled nylon with a beautiful surface finish.
Onyx FR™
Flame-retardant, UL Blue Card, V-0 (self-extinguishing) at thicknesses greater than or equal to 3mm.
Onyx ESD™
High-performance static-dissipative, stronger, stiffer version of Onyx.
Onyx FR-A™
For aerospace and automotive with lot-level traceability, parts meet 14 CFR 25.853.
Which Markforged Continuous Fibre Material?
Kevlar
Lightweight, durable, strong, good for parts with repeated and sudden loading.
Carbon Fibre
Strength of aluminium but half the weight, highest strength to weight ratio of the Markforged range.
Fibreglass
High strength at an accessible price to reinforce prints for strong, robust tools.
HSHT Fiberglass
The strength of heat tolerance of aluminium for parts loaded in high operating temperatures.
Other Composite powders and filaments
Nylon 11 CF
Ideal for printing stiff, strong and lightweight end-use parts.
PC
Tough with outstanding strength, stiffness. Offers impact resistance.
PA-CF
High strength, stiffness and durability.
PC-ABS
High impact strength, stiffness, and heat resistance.
PEEK-CF
Chemical resistance, toughness, very high stiffness, hydrolysis and superheated steam resistant.
Interested in Composite or Continuous Fibre materials?
Call the team now for advice about which additive manufacturing material/technology combination is most suitable.
Printing Examples
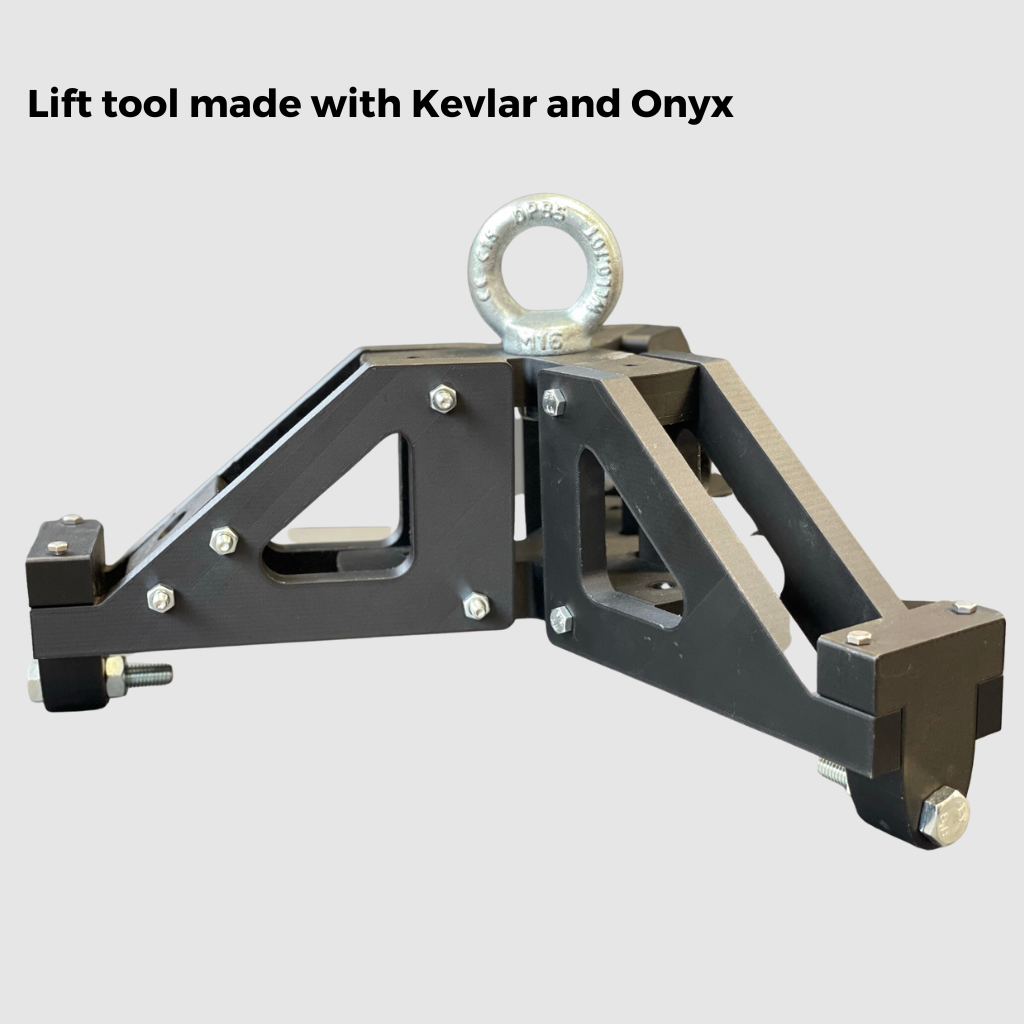



Order Your Composite Materials for 3D Printing 3D Printed Parts
Get Started With 3D, Without The Investment, Make Use Of Our Custom 3D Printing Service
Composite 3D Printers
Additive-X | Your experienced additive manufacturing partner
Advice • Samples • Benchmark prints
Request a call from our team, or contact us now
FAQ’S
Commonly asked questions about Composite and Continuous Fibre Reinforced 3D Printing
Composite materials in 3D printing offer properties and characteristics that aren’t always found in traditional materials. These composites consist of a polymer matrix infused with reinforcing fibres, typically ranging from 10% to above 30% by weight. The presence of these composite fibres significantly enhances the strength and durability of the printed parts. Unlike standard 3D printing materials, composite machines have the capability to incorporate continuous strands or fibres into the print, similar to the concept of reinforced concrete.
Printing with composite materials can impact printhead and Bowden tube longevity. Composite filaments contain abrasive particles that erode these components over time. Printheads suffer wear, affecting print quality. But printers that are designed for composite printing have specialized modules to resist abrasion. As well as printheads, Bowden tubes, common in remote extruders, experience friction-related wear which can lead to roughness and even clogging. All of this can be mitigated, however, by ensuring regular tube replacement and use of specialist printing components.
The base materials used in composite 3D printing often include Nylon, a versatile and widely used thermoplastic known for its excellent mechanical properties and durability. Additionally, some of the common composite materials belong to the PAEK family, which includes high-performance polymers like PEEK (polyetheretherketone) and PEKK (polyetherketoneketone). These PAEK-based composites exhibit exceptional thermal stability, chemical resistance, and mechanical strength, making them ideal for demanding applications in industries such as aerospace, automotive, and healthcare.



